What is eduScrum?
July 14, 2021 • 17 min to read
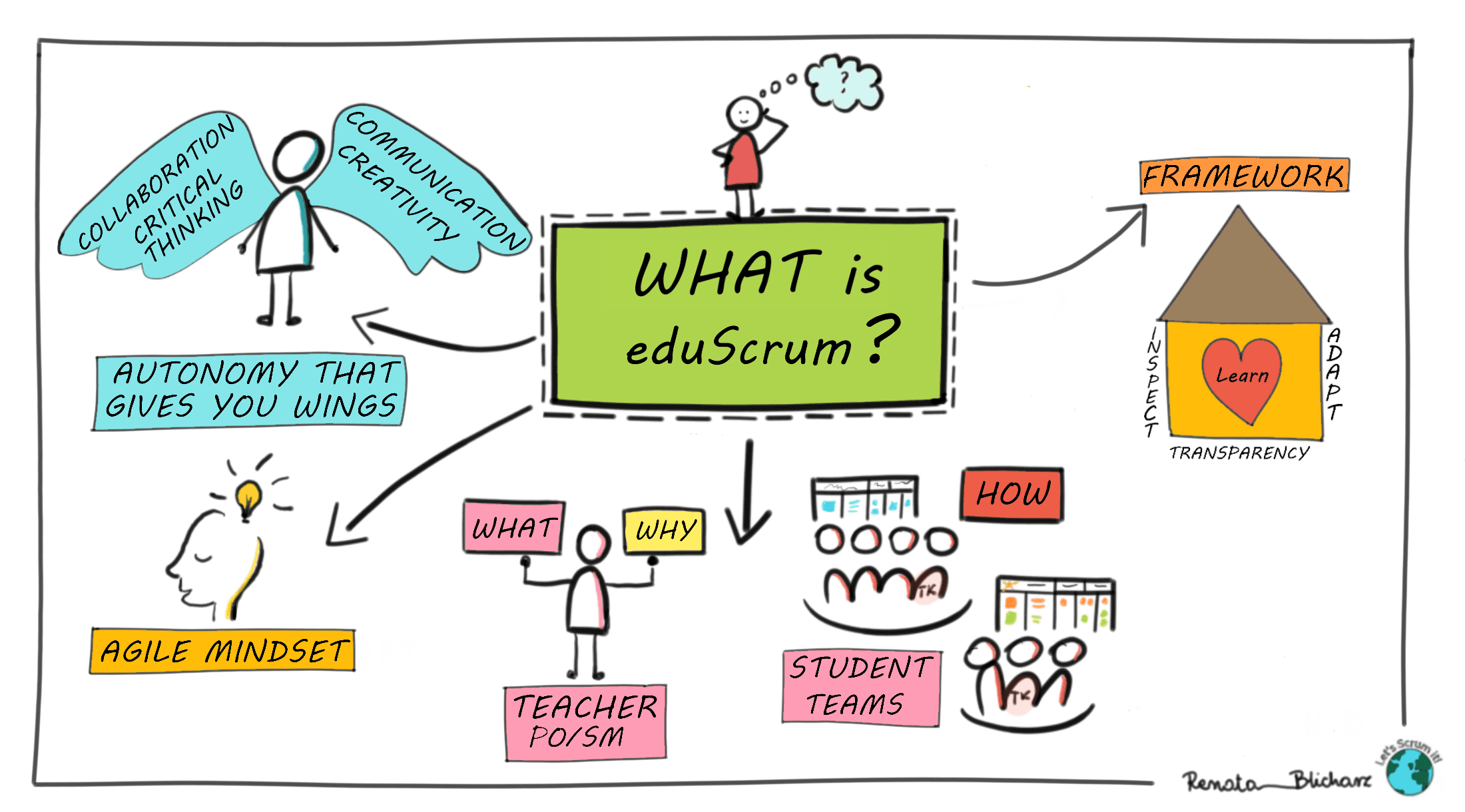
Jump in here to explore eduScrum framework - innovative way of working with students. I explain in this post what is the foundation of the framework and how it relates to roles, events and artifacts.
Table of Contents
Introduction
In my last post I explained WHY we need eduScrum in education. Today I would like to demonstrate WHAT is eduScrum. Before I will move on, I want to ask you a question:
What is the value of Education in your life? Does it matter to you?
I've done some research to find out what the impact of education on the world is. In the publication "The wellbeing effect of education" (unfortunately it doesn’t exist anymore on their website) written by Economic & Social Research Council we can read that:
Education has become one of the clearest indicators of life outcomes such as employment, income and social status, and is a strong predictor of attitudes and wellbeing.
Education is often used by people to shape their ‘social identity’, framing their understanding of themselves and their relationships with other people.
How does education affect the world?
- Removing poverty
- Shaping a better society - better understanding of moral & ethical problems
- Encourages innovation & creativity
- Leads to economic prosperity
- Helps to learn from the mistakes of the past…
I could continue writing and that list would never end. Education has a huge impact on our lives no matter what we do and who we are.
That’s why it is so important to analyze how we educate students and what we can do to improve their learning process and help them to thrive.
eduScrum is not a silver bullet, but it can help to develop 21st century skills and address some issues that we experience in education.
![]()
The history of eduScrum
It starts with a bottle of beer and a barbeque in the summer (June) of 2011 with Mark Reijn. Mark just finished a Scrum course given by Jeff Sutherland at the company Schuberg Philis in Amsterdam, where Mark works as a software engineer. Mark was very enthusiastic about Scrum, inspired by Jeff and he explained Scrum to me on one single paper.
He was the sparkle who put me on fire. In August 2011 I started one class using Scrum to try-out if it works in the classroom. In the beginning I was surprised that it was working. So, I began to use Scrum in all my classes with success. And so the name eduScrum was born.
That’s how the origins of eduScrum were described by the founder of the framework - Willy Wijnands.
eduScrum is the child of the Scrum, initially created to develop complex IT products.
Scrum is currently described in the Scrum Guide as:
a lightweight framework that helps people, teams and organizations generate value through adaptive solutions for complex problems.
What is really interesting, in Willy’s history we can observe the empirical approach, which is the foundation of Scrum. His knowledge came from experience - he verified how Scrum works at school and adapted it to the education environment creating a new framework - eduScrum.
The overview of eduScrum
Based on the eduScrum Guide:
eduScrum is a framework within which teachers and pupils tackle complex, challenging problems and pursue learning goals of the highest possible value in a productive and creative manner.
I will be quoting eduScrum Guide in this article many times, because it is the best source of knowledge describing that framework.
The most important aspects of eduScrum are:
- Teacher prescribes "Why" and "What", but doesn’t define "How" (processes, techniques).
- Students have autonomy and take responsibility for their own learning process. Responsibility is delegated from the teacher to students.
- Learning is central in eduScrum - students learn how to collaborate better, learn smarter and learn more about themselves.
- eduScrum not only improves the learning results, but also helps students discover their strengths and learn how to work together in teams.
- Important aspect of eduScrum for teachers is to have an Agile mindset to trust students and give them freedom to choose how they will be achieving the learning objectives.
- Quality of students' achievements is constantly evolving during a school year as a result of ownership and continuous improvement process.
eduScrum & Empiricism
eduScrum, similar to Scrum, is founded on empiricism - theory that states that knowledge comes from experience. The framework uses 3 pillars as a foundation of all activities:
1) Transparency
- There are common standards and language (including definitions) between teams & teachers to communicate and share the understanding of the learning process.
- Students & teachers are honest in regards to any issues that they experience during the learning process.
- Tools used by students are transparent and visible in the classroom.
2) Inspection (Review)
- Progress towards the learning objectives is frequently reviewed in order to recognize improvements, required changes.
- Reviews are performed by both - teams and teachers in the classroom.
3) Adaptation
- Based on the review, when students or teachers recognize that some aspects of the learning process are not working well, they can make adjustments.
- The adjustment should be done as quickly as possible to avoid further issues.
I know that these terms and explanations can be unclear to you for now. Hopefully you will understand it better once I explain all the elements of eduScrum.
In simple words - empiricism means transparency in the classroom, frequent reviews/checks to see if improvements are required and based on that experience making changes.
eduScrum Roles
The eduScrum framework, such as the Scrum framework, consists of teams and their associated roles, ceremonies, artifacts and rules. Each component within the framework serves a specific purpose and is essential for the use and success of eduScrum.
I will try to explain to you all roles, ceremonies/events and artifacts below.
eduScrum framework includes the following roles:
- The Teacher (Product Owner/eduScrum Master)
- The Student Team
- The Team Captain
- Let’s start with The Teacher.
Role of The Teacher is a hybrid of Product Owner & eduScrum Master. In eduScrum it is different from the traditional approach. They are still responsible for monitoring and improving the academic outcomes - they need to test and assess the personal development of students.
However, their role in the learning process evolves. They are no longer the only source of true/knowledge for students. The Teacher should determine WHAT are the learning objectives, their Celebration Criteria and WHY students need to achieve them. While students decide HOW they will do it.
What does it mean for teachers? They need to trust their students and give them more space for discovery & failure on their own. It requires from them developing the Agile Mindset.
Does it mean that students are left alone? Of course not.
- The Teachers should facilitate the learning process & observe how teams and individuals are doing.
- They should still be subject matter experts who can support, answer the questions & guide. There is still space in the process for giving a lecture and explaining subjects that are not clear for students.
- But what teachers should not be doing is giving the solution straight away and solving problems for students.
- The important part of the Teacher role is to stimulate the learning environment by encouraging cross-team collaboration, inspiring students, creating a safe & positive environment.
- Additionally, the Teacher protects students from external disturbances and pays attention to issues within the teams. The framework gives them more visibility on individuals who require their support.
- The Teacher should also coach Team Captains & promote eduScrum values & Agile philosophy in the classroom.
![]()
- The next role in the eduScrum framework is The Student Team.
The student team consists of independent students who do the work together in order to achieve the set learning objectives at the end of the sprint in accordance with the Celebration Criteria.
The Student Team should consist of 4 or 5 team members. Enough to have all skills required to achieve learning objectives, but not too many, to avoid coordination and communication issues.
What is the role of the Student Team?
- They are responsible for their own learning process & meeting the Celebration Criteria given by the teacher.
- The Team should have enough skills to be self-organized. They decide HOW they will achieve the learning objectives.
- What is important, they are responsible for the outcomes as a whole. It means that if one person has some issues, they need to all support them and try to achieve learning objectives together.
- The Student Team tracks their progress by themselves.
- Every Team member has also space to use their qualities or develop some new skills within their team.
- They use the Flap, Definition of Doing, Definition of Communication & Definition of Fun to manage their work & make the learning process interesting.
![]()
Source:eduScrum library
- The last role in the eduScrum is The Team Captain
In each Student Team there is one member who plays the role of Team Captain. Their main role is to ensure that The Student Team performs well. In the initial version of the eduScrum the role of the Team Captain was described as an eduScrum Master, but it didn’t fully reflect tasks and responsibilities of the role.
The Team Captain is selected at the beginning of the Sprint during the team formation. They can be chosen by the teacher, students or just randomly.
What are the main responsibilities of the Team Captain:
- Making sure that "Flap" (eduScrum board) is updated, available when needed and visible. They need to ensure that the progress of the team is transparent.
- Facilitating eduScrum events when required.
- Helping the team to remove impediments, letting the teacher know about them.
- Starting the cross-team collaboration.
eduScrum events/ceremonies
Similar to Scrum, eduScrum uses timeboxed ceremonies designed to enable transparency, inspection and adaptation. They also help in predictability and increase using the time efficiently.
I will write a short description of every event, but you can find more details about them in eduScrum Guide. You can also expect posts in the future that will help you to understand each ceremony better.
In the meantime you can also refer to my past posts related to Scrum about:
Of course there are differences, because eduScrum is adjusted to the Education environment, but some of the main ideas are similar.
![]()
####Source:https://www.eduscrum.nl/resources
eduScrum - Sprint
The heart of eduScrum is a sprint, a composite set of learning materials that ensure that the learning objectives are achieved. A sprint can be a context-rich lesson series, a project, a chapter from a book and so on. In general, a sprint will coincide with the length of a semester or period, although this is not a requirement.
It is timeboxed to approximately seven weeks, but it depends on the school and class schedule.
The Sprint consists of all other ceremonies that I will be describing below.
eduScrum - Sprint Planning
The sprint planning meeting is a meeting within a timebox of two hours for a sprint of approximately 2 months.
It is the event happening at the beginning of the Sprint. It consists of:
- Team formation
- Learning objectives
- explanation what are the expectations, objectives, Celebration Criteria
- Work planning
1) eduScrum Team formation
The Sprint Planning starts from the formation of the Student Teams. Every student fills out the questionnaire with their main qualities and skills.
Before the teams are created either teacher or students select Team captains. It can be also done randomly. They select team members anonymously based on their qualities and skills. The goal of the team formation is to have team members with complementary qualities & skills. Teams should have also balanced gender distribution and they should not be based on friendship.
![]()
2) Learning objectives
During the learning objective part the teacher explains to students what are their expectations and what needs to be delivered by the end of the Sprint.
The Teacher should explain the vision of the Sprint, the overview of the assignment, but also why students need to learn it - the purpose. It’s also time for the teacher to talk about the number of lessons within the Sprint, what are the most important dates like: submission, test dates.
3) Work planning
In order to plan their work, Student Teams receive the content of the assignment from the Teacher - list of stories (sub-topics that need to be completed within the Sprint). Stories should include:
- Learning objectives based on the Curriculum and government expectations
- Celebration Criteria that need to be met to complete the story
Once teams have an idea what are the expectations for the Sprint, it’s time for them to plan their work. The Student Team uses "Flap" - eduScrum Board, flipchart as a visual representation of their plans and later their work. They write on the Flap:
- Name of the Project
- Stories & Celebration Criteria that they received from the Teacher
- Team Name
- Team Members
![]()
Source: eduScrum library
For each story, the Student Team creates tasks representing all work that is required to complete the story. Stories and tasks should be ordered chronologically based on priorities discussed with the teacher. Once all tasks are created, students use the Planning Poker technique to estimate their work. They assign a number of points to each task depending on the complexity of the task and skills within the team.
After estimation the Student Team draws Run Up Chart - graph with number of lessons/weeks on horizontal axis and story points on the vertical. To recognize how many story points they need to complete each lesson (what should be their ideal velocity), they divide the total amount of points by lessons and draw the ideal line. The Run Up Chart is the tool used by students to track their progress.
Additionally students create their:
- Definition of Doing for completion of tasks - work agreements within the team specifying when the work is "Done" e.g. task was discussed with all team members, everyone in the team did a quiz, celebration criteria are met, etc.
- Definition of Communication - to explain how students will communicate with each other (created during Covid time and extremely important for online learning) .
- Definition of Fun - explaining what is the best environment that can help students to enjoy learning and have fun e.g. laughing together, celebrating achievements together, bringing sth to eat etc.
At the end of the Sprint Planning session, Student Teams should be able to explain to the Teacher what they are planning to do to achieve the learning objectives.
It is possible that students will struggle with creating tasks at the first time. It’s not always natural for them that they have the freedom to decide by themselves how to work. In that case, it's the teacher's role to guide them & give the necessary support.
Stand Up
The stand up is a five minute time- boxed event for the student team to synchronize activities and make a plan for the next meeting.
The Team Captain should ensure that the team has a meeting and they keep it within the time-box. The event takes place at the beginning of each lesson.
During the meeting, each student team member explains the following:
Stand Up is an opportunity for the Student Team to monitor their progress and discuss any issues, dependencies.
- During the meeting the Students Team uses "Flap" to track their progress. Flap is constantly updated and students move tasks that they are working on between statuses "To Do", "Busy" and "Done". During Standup they have an opportunity to recognize how many tasks they have done and what is still outstanding.
- Every lesson they mark on the Run Up Chart how many story points were completed and compare it to the ideal line that they drew initially on the planning session.
- Stand Up is also the time when the team communicates Impediments listed on the Flap. Impediments can be added on the sticky notes to the Flap at any moment of the Sprint.
![]()
Source: eduScrum library
Sprint Review
Sprint Review is the event that takes place repeatedly during the sprint - The Student Teams present others what they achieved. The form of the final presentation or smaller reviews depends on the learning objectives and Celebration Criteria. The main goal of Sprint Review is to inspect the progress towards the learning objectives, receive feedback and adjust if required.
In eduScrum we want to give and receive the constant feedback in a "dolphin" (incremental) style and avoid a situation when there is no transparency about the progress over the Sprint. The below picture is a great representation of this style of learning.
Source: eduScrum library
Sprint Retrospective
Once the Sprint is coming to the end, it’s time for the last, but really important ceremony in the eduScrum - Sprint Retrospective. The purpose of the event is to analyze how the last sprint went with regard to people, relationships, processes and tools. It is a moment for personal and team reflection that can help students to improve themselves in the next Sprint.
The Sprint Retrospective in eduScrum consists of:
1)Team evaluation:
- Reflection on the team - tools, the way of working and what are the areas for improvement: what went well and what shouldn’t be done anymore
- Evaluation of teammates - feedback to explain what skills they used over the Sprint, what went well and what they should work on.
This part can be organized also on the class level if teams are changing every Sprint.
2)Personal reflection:
- Similar to team reflection, students should evaluate themselves individually by asking the questions about skills - what they did well, what skills they developed and what they need to work on in the future.
The outcomes of the Sprint Retrospective should include the understanding of achievements and ideas for improvements on the team and individual level. That is the opportunity for each student to grow as a team member and as an individual.
Summary
I know that it is not a short post, so congrats if you’ve managed to come to this point!
![]()
Few points to remember about eduScrum:
- eduScrum is a framework created by Willy Wijnands in 2011 that gives the students ownership for their own learning process.
- Teacher give the answer for questions "Why?" and "What?", but students have a space to decide "How" they will achieve their learning objectives.
- eduScrum is based on Scrum and founded on Empiricism that uses 3 pillars: Transparency, Inspection (Review) and Adaptation.
- eduScrum roles are: The Teacher (Product Owner/eduScrum Master), The Team Captain, The Student’s Team
- eduScrum ceremonies/events are: Sprint, Sprint Planning (Team formation, Learning Objectives, Work Planning), Standup, Sprint Review, Sprint Retrospective (Team evaluation, Personal Reflection)
- eduScrum artifacts are: Content of assignment (stories with Celebration criteria), The Flap - eduScrum Board, Definition of Doing, Definition of Communication, Definition of Fun
Thank you for reading my article. What do you think about eduScrum? Is there anything that surprised you?
Please let me know if you find this topic interesting and what parts you would like to explore more. If you would like to learn more about eduScrum, I invite you to my eduScrum Basic Training.
Would you like to read more about education?
Sign up for the Newsletter & join Let's Scrum it community!